·
That means we want to redesign the DAO such that it should work with
single instance of Driver class irrespective of the number of clients and
requests.
·
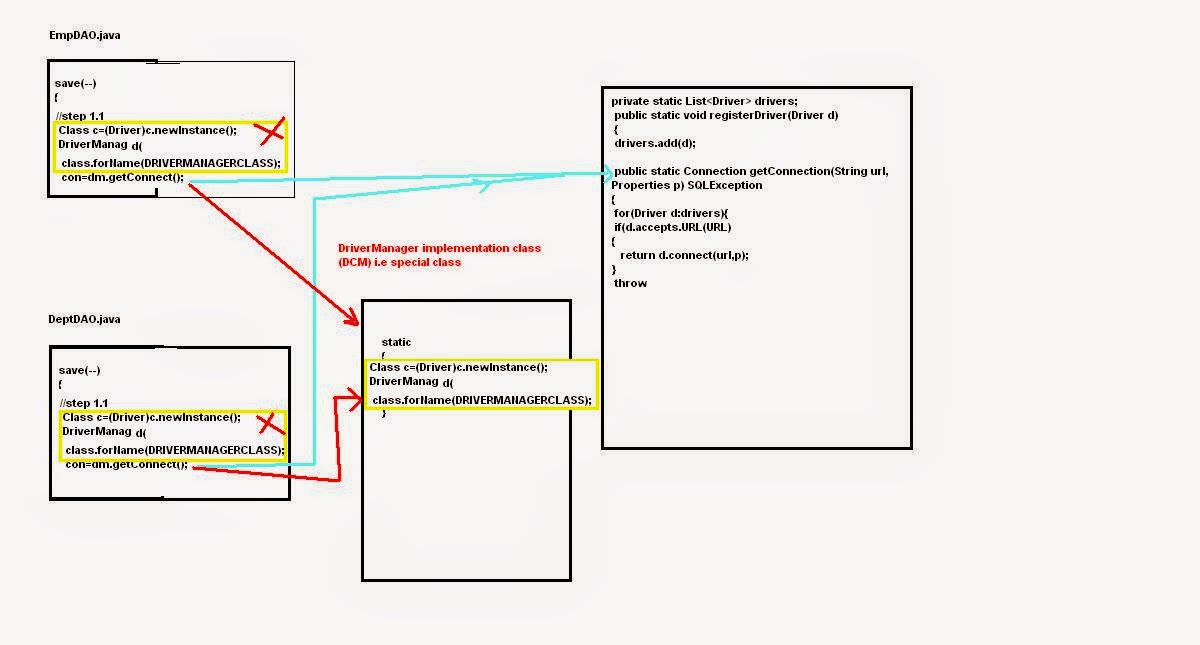
To address this requirements JDBC introduces DriverManager class
Q: What is Driver Manager class?
The
java.sql.DriverManager is a factory class that is designed to create the
Connection Managing the Driver objects.
Why DriverManager?
Ans: to centralize the code(
means connect() method) creating the Connection using the Driver object. So
that we can avoid multiple instances (objects) of a Driver class to create.
Here the code means connect() method.
Q: How
DriverManager functions?
We know that the basic
functionality of the DriverManager is to create the Connection managing the
Driver object. The getConnection() method will create connection using
registered Driver object.
Working with
DriverManager
Fig: DriverManager
FactoryClass(.JPG
The following two steps are
involved in doing this:
Step1: Register the Driver to
DriverManager
Step2: Invoke the getConnection()
to get the Connection
Step1: Register the Driver to DriverManager
·
The following static method of DriverManager is
used to do this: registerDriver(Driver
d);
·
We want to do this only once for each driver to
use in the application.
·
The jdbc specification includes a rule to have a
static block in the Driver implementation class that should create an object if
itself and register it to the DriverManager.
Example: the following snippet shows the code of
OracleDriver class.
//it is a internal code (readymade ), just we are writing to
awareness only, we have to use not to write)
public class OracleDriver implements Driver
{
Static
{
DriverManager.registerDriver(new OracleDriver());
}
--
--
}
·
From this discussion we understand if we can
load the driver class into the JVM it
results to execute the static block of the same class which registers this
driver object to DriverManager.
public class ClassLoadTest {
public static void main(String
args) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("In main
method");
}
}
class Test1
{
static
{
System.out.println("Test1
static block");
}
}
Output:
In main method
Ex2:
public class ClassLoadTest {
public static void main(String
args[]) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("In main
method");
for(int
i=0;i<10;i++)
{
Class.forName("Test1");
}
}
}
class Test1
{
static
{
System.out.println("Test1
static block");
}
}
In Main method
Test1 static block
0
1
.
10
Note:
Class c=Test1.class ;//for dynamic we can not use this
Class c=Class.forName(Test1); both are same to load the
class into JVM , when you know about the class name go for Class
c=Test1.class;//it is implicit field like super, this, class
The following 3 points are important to consider with respect
to class loading:
1.
static
block executing all the time of loading the class into JVM. Note: this is not
true always in some jvm’s the static blocks are delayed to execute on first
access to any member of the class.
Example:
public class ClassLoadTest {
public static void main(String
args[]) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("In main
method");
/*for(int
i=0;i<10;i++)
{
Class.forName("Test1");
}*/
Class
c=Test1.class;
System.out.println("c");
System.out.println("Test1 is
loaded");
System.in.read();//waits until
user press enter
System.out.println("Count
:="+Test1.count);
}
}
class Test1
{
static int count=10;
static
{
System.out.println("Test1 static
block");
}
}
In main method
c
Test1 is loaded
Test1 static block
Count :=10
2.
A class is loaded into the jvm on first access
to any member of class , this is implicit (or)
·
Use class.forName(-); //this is explicit
·
Use ‘class’ implicit field
3.
Invoking
the class.forName(-); with the same input for multiple times will not
result loading class for multiple times.
Step 1.2: invoking the getConnection() method:
·
After we register the driver to DriverManager we
can use any of the following static
methods of DriverManager to get the Connection.
Connection
getConnection(String url, Properties jdbcprops) throws SQLException
·
This method finds the registered drivers that
can use the given url for getting the connection. If found use it to get the
connection. Otherwise throw SQLException ‘No suitable Driver Found’
·
This method is just a convenience method. This
method internally creates the properties object setting the given username and
password, and invoke above method.
Connection
getConnection(String url, String db_user, String db_password) throws SQLException
·
This is also a convenience useful in case if
there are to no properties describe for getting the Connection
Fig: Approach2DriverManager.JPG
4 jdbc step1 from myrajendra

No comments:
Post a Comment